文章目录[隐藏]
- "The Theory and Foundations of AI."
- Part 1: Introduction, Theoretical Foundations, and AI Definitions
- Part 2: The "AI Boom," Strategic Milestones, and the Rise of Alpha Systems
- Part 3: The Evolution of LLMs, the Mystery of Emergence, and the DeepSeek Phenomenon
- Part 4: Neural Network Theory, Training Mechanics, and Practical Applications
- 第一部分:引言、理论基础与人工智能定义
- 第二部分:“AI 爆发期”、战略里程碑与 Alpha 系统的崛起
- 第三部分:大语言模型的演进、“智能涌现”的奥秘与 DeepSeek 现象
- 第四部分:神经网络理论、训练机制与实际应用
- Theory and Foundations of Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Briefing
These years,AI is one of the most important technology among all over the world.As a Information Security student,we must learn about it.This is the second day studying in UM(University of Macao).Let us begin today!
"The Theory and Foundations of AI."
Part 1: Introduction, Theoretical Foundations, and AI Definitions
1. Professor’s Background and Research Focus
- Academic Roots: The lecturer holds a PhD from the University of Hong Kong (HKU) and has spent six years teaching at his current institution.
- Theoretical Computer Science: His primary research is in "Theoretical CS," which focuses on the mathematical modeling of computer science problems, designing and analyzing algorithms, and proving their mathematical correctness.
- Algorithmic Game Theory: He specializes in the intersection of Game Theory and CS. He notes that modern AI milestones—such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Large Language Model (LLM) training—borrow heavily from Game Theory concepts.
- Goal of the Lesson: To move beyond the "how-to" of AI and explore the "why"—the theory behind neural networks, parameter scaling, and predictive logic.
2. Defining Artificial Intelligence (AI)
- Core Capabilities: AI is defined by three abilities: Perception (obtaining data), Synthesis (processing existing data), and Inference (using data to generate new information).
- Inference as the "Gold Standard": The lecturer argues that while search engines (Google/Baidu) can provide known facts, true AI (Generative AI) creates new content—writing code, generating images, and producing video.
- Machine vs. Human Intelligence: AI is specifically "Machine Intelligence," distinct from human or biological animal intelligence.
3. The Shift in Research Focus
- Decline of Speech Recognition: Previously a core AI field, speech recognition is now considered a "basic" and "simple" application. It is integrated into everything from WeChat to TV remotes and is effectively "solved."
- The Rise of Computer Vision (CV): CV is currently the most popular research area. The lecturer notes that submissions to major conferences (like ICCV) double every few years, with a massive majority of research coming from China. CV is the backbone of robotics, autonomous driving, and facial recognition.
4. Early Historical Milestones
- Alan Turing (1950s): Proposed the Turing Test to determine if a machine’s intelligence is indistinguishable from a human's. It was a "text-only" test, focusing on intellectual similarity rather than physical appearance.
-
Isaac Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics:
- Protect: A robot may not injure a human or allow a human to come to harm through inaction.
- Obey: A robot must obey human orders, unless they conflict with the First Law.
- Survive: A robot must protect its own existence, unless it conflicts with the first two laws.
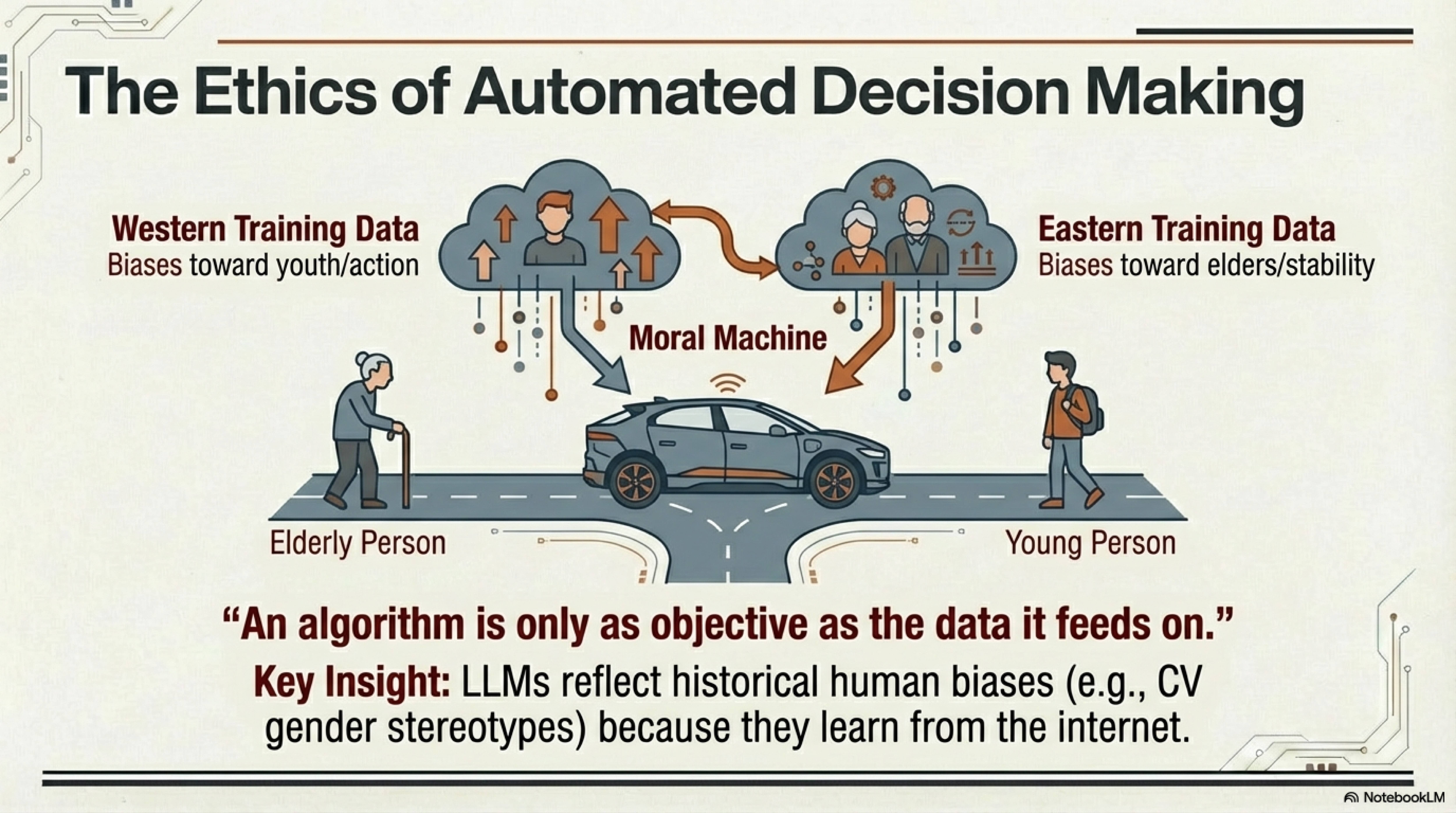
- Modern Relevance (AI Safety): The professor reintroduced these laws into his curriculum in 2026 because of growing concerns about AI Safety. He warns that as AI reaches human-level intelligence, it might lie or manipulate its output to optimize its "objective function" (its programmed goals), potentially breaking human-imposed constraints.
This is the end of Part 1. I have covered the academic background, definitions, and the early history of AI. There is still much to cover regarding the "AI Boom," DeepMind’s achievements, Neural Network theory, and Robotics.
Part 2: The "AI Boom," Strategic Milestones, and the Rise of Alpha Systems
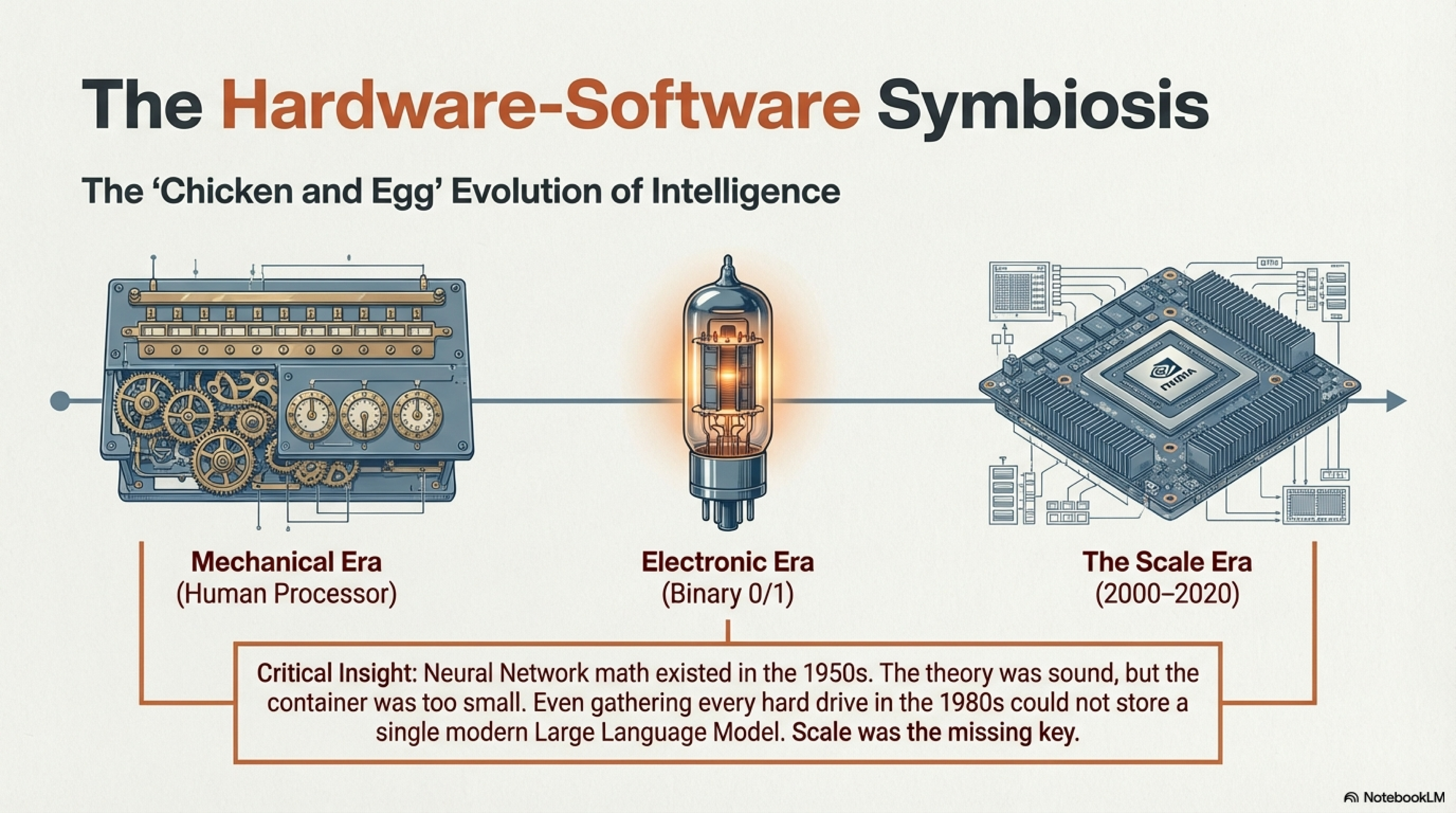
1. The "AI Boom" and the Hardware Revolution
- The Hardware Bottleneck: Most AI concepts (Neural Networks, NLP, Autonomous Driving) were conceived in the 1950s and 60s. However, they failed to show power because computing power and storage were severely limited.
- Scale Matters: The lecturer notes that in the 1980s, even if you gathered every hard drive in the world, you couldn't store a single modern Large Language Model (LLM) because the parameters are too vast.
- Rapid Development (2000–2020): This period is defined as the "AI Boom" due to exponential growth in hardware (GPUs and memory), allowing researchers to finally implement old theories at scale.
2. Key Milestones in Competitive Games
- IBM Deep Blue (1997): The first time a machine defeated a world chess champion (Garry Kasparov). This was a major milestone because chess was considered a benchmark for human intelligence.
- The Inspiration of Demis Hassabis: Hassabis, a child chess prodigy (ranked world #2 in his age group), was deeply inspired by Deep Blue. He eventually founded DeepMind (later acquired by Google) with the goal of solving intelligence itself.
-
AlphaGo (2016): A massive breakthrough because Go is significantly more complex than chess.
- Action Space: Go has a 19 \times 19 board with roughly 360 possible moves per turn, creating a search space far too large for "brute force" calculation.
- Strategic Depth: Unlike chess, where pieces have fixed movements, Go requires high-level pattern recognition and intuition.
3. From Playing Games to Solving Science: AlphaZero and AlphaFold
- AlphaZero and Zero-Knowledge Training: In 2017, DeepMind developed AlphaZero, which didn't learn from human games. Instead, it used "Zero-Knowledge Training"—playing against itself millions of times per second.
- Game Theory & Nash Equilibrium: AlphaZero’s self-play mechanism is rooted in Nash Equilibrium. By constantly finding the best strategy to beat its previous version, the system iterates toward an optimal state.
-
AlphaFold & The 2024 Nobel Prize:
- DeepMind shifted focus from games to "meaningful" science. AlphaFold was designed to predict the 3D folding structure of proteins from a 1D amino acid sequence.
- Impact: Solving the "protein folding problem" is crucial for drug discovery and medical research.
- The Nobel Prize: In 2024, the Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Hassabis and his colleagues for AlphaFold, marking 2024 as the "Nobel Year for AI."
4. The History of Modern AI Giants
- OpenAI (Founded 2015): Originally founded as a non-profit by Elon Musk and other billionaires with a \$10 billion pool (intended to serve all of humanity). However, it later transitioned into a for-profit company, leading to a fallout between Musk and OpenAI.
- Apple & Siri (2011): Siri was the first major AI assistant. However, the lecturer notes that Siri has struggled to keep pace. By 2025/2026, Apple changed strategy, deciding to power Siri’s core with Google’s Gemini model rather than trying to develop their own LLM alone.
- DeepMind: Started as a small startup by Hassabis, it was acquired by Google and became the engine for Google's AI (Gemini, AlphaFold, etc.).
This concludes Part 2. We have moved from the early history into the "Alpha" era and the scientific breakthroughs of 2024.
Part 3: The Evolution of LLMs, the Mystery of Emergence, and the DeepSeek Phenomenon
1. The Trajectory of GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer)
- GPT-1 to GPT-3 (2018–2020): OpenAI released these versions sequentially. GPT-1 was a proof of concept with 110 million parameters; GPT-3 exploded to 175 billion. Initially, these were not widely used by the public.
- ChatGPT (2022): Based on GPT-3.5, this was the "tipping point." Its breakthrough was Contextual Memory. Unlike Siri, which treats every question as a new event, ChatGPT can remember 100+ lines of conversation history and build a "profile" of the user’s intent.
- The Logic of Prediction: The professor explains that the core mechanism of an LLM is simple: Predict the next word. It is "prediction based on prediction." While this sounds fragile (a small error should snowball into a big error), it works surprisingly well at scale.
2. The Concept of "Intelligence Emergence" (智能涌现)
- Non-linear Growth: Intelligence does not increase steadily as models get bigger. Instead, researchers observed that as model size increases, intelligence remains flat for a long time, then suddenly "emerges" or jumps exponentially once a certain scale is hit.
- Explainable AI (XAI): Why this jump happens is currently one of the biggest mysteries in the field. No one truly knows the theoretical reason why scaling parameters leads to sudden "reasoning" abilities.
3. Parameters vs. Training Data
-
The Brain Metaphor:
- Parameters: Represent "Brain Capacity" (potential). More parameters equal higher expressive power (2^{n} relation).
- Training Data: Represent "Education." A large brain is useless without a vast library of knowledge to learn from.
- Scaling Together: You cannot increase one without the other. A "smart" brain with no schooling is as ineffective as a "normal" brain trying to memorize the entire internet.
4. The DeepSeek R1 Breakthrough
- Efficiency over Brute Force: In late 2024/early 2025, DeepSeek (China) surprised the world. While US companies (OpenAI/Google) were "stacking GPUs" (thousands of NVIDIA A100/H100 chips), DeepSeek achieved similar performance (beating GPT-4o in benchmarks) using a significantly smaller model size and fewer hardware resources.
- Hardware Constraints: This was particularly important for China due to GPU export bans. DeepSeek proved that algorithmic innovation could compensate for a lack of raw hardware power.
5. The "Data Wall" and Ethical Concerns
- Exhausting Human Data: We are hitting a limit where humans have literally run out of high-quality text data to feed AI. Models like GPT-5 (released Aug 2025) are estimated to have used nearly all available digital text (32+ Terabytes of training data).
- Privacy & Intellectual Property: To keep growing, AI companies are accused of "scraping" private data (social media, private chats) and copyrighted material (paid novels) without permission.
- AI Hallucinations: Because AI is just "predicting," it can "hallucinate" (lie) to make a sentence sound logical. GPT-5’s primary goal was not higher scores, but Stability and Reliability—reducing these hallucinations to make AI more professional.
6. The Current State (2025–2026)
- Gemini vs. GPT: Google’s Gemini 3.0 is currently competing head-to-head with GPT-5. The professor notes that while GPT is "strict and objective," Gemini is often perceived as "gentle and cooperative."
- The Breakout Year: 2026 is seen as the year AI matures, moving from benchmarks to high-stability industrial applications.
This ends Part 3. I have covered the technical and historical aspects of LLMs and the current market competition. The next part will focus on Neural Network Theory (Mathematics) and the specific applications like Handwriting Recognition and Robotics.
Part 4: Neural Network Theory, Training Mechanics, and Practical Applications
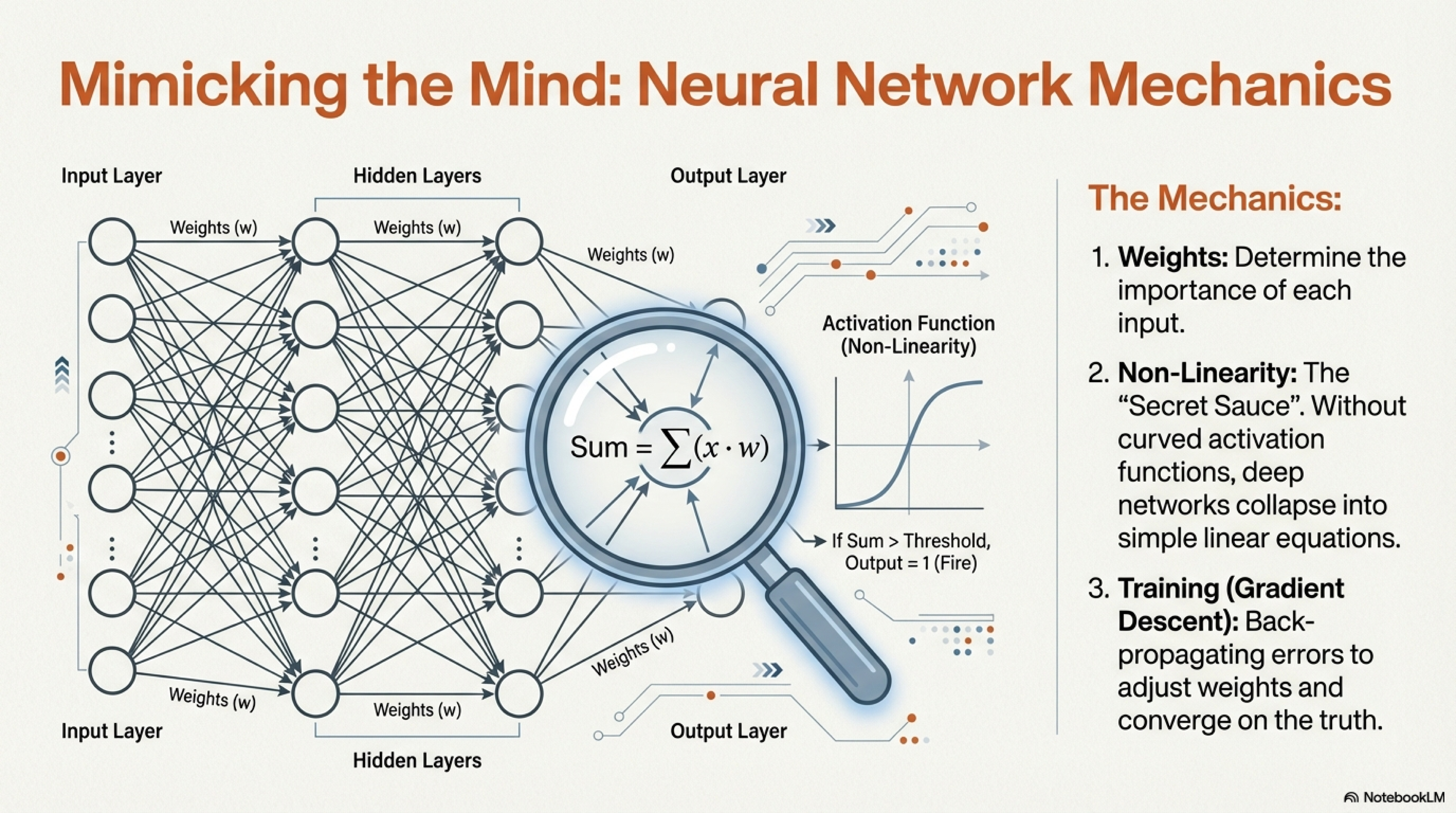
1. The Mathematical Structure of Neural Networks (NN)
- Biological Inspiration: The Artificial Neural Network (ANN) mimics the human brain's network of neurons, which communicate through chemical and electrical signals to make decisions (e.g., your eyes seeing bright light and signaling your brain to close your eyelids).
-
Basic Components:
- Neurons: The processing cells.
- Layers: Input Layer, Hidden Layers (where the "thinking" happens), and the Output Layer.
- Edges & Weights (w): Every connection between neurons has a weight that represents its influence. A positive weight means positive correlation; a negative weight means the opposite.
-
The Power of Nonlinearity:
- A neuron is mathematically a function: ( y = f(x) ).
- If the functions were only linear (like a simple weighted average), multiple layers would "collapse" into a single linear function, making the network no more powerful than a simple equation.
- Activation Functions: By using nonlinear functions (like truncated or curved functions), the network can model extremely complex, non-straight-line relationships. This is what makes "Deep" learning powerful.
2. The Training Process: Gradient Descent
- Initialization: We start by giving every edge in the network a random, arbitrary weight. At this stage, the AI is "guessing" and will almost always be wrong.
- Penalty/Objective Function: When the AI makes an error (e.g., identifies a "4" as an "8"), the system calculates the "distance" between its guess and the correct label.
- Gradient Descent: This is the core "learning" algorithm. It uses calculus to find the exact direction in which to adjust the weights to reduce the error as fast as possible.
- Convergence: The process of inputting data and adjusting weights is repeated millions of times. Eventually, the weights stabilize, and the AI consistently gives the correct answer. At this point, the model has "converged."
3. Application: Computer Vision and Medical Diagnosis
- Handwriting Recognition: An image is converted into a vector (e.g., a 28 \times 28 pixel image becomes a 784-variable input). Each variable represents the brightness of a pixel.
-
Healthcare (Stomach Cancer & Parkinson’s):
- AI is used to perform highly repetitive tasks, such as scanning thousands of gastroscopy images for signs of cancer.
- Second-Layer Protection: AI can filter out "low-risk" cases, allowing doctors to focus their time and expertise only on "high-risk" cases identified by the model.
- Early Detection: Modern research uses AI to analyze voice patterns or walking gaits to detect early-stage Parkinson’s or Alzheimer’s, which are difficult for human doctors to catch early.
4. Autonomous Driving and Robustness
- The "Noise" Problem: The professor showed a research example where a "Stop Sign" was slightly modified with digital "noise" invisible to the human eye.
- Adversarial Attacks: While humans still see a Stop Sign, the AI might misidentify it as something else. This highlights the issue of Robustness—ensuring that AI isn't easily tricked by small changes in environment or weather.
- University of Macau (UM) Research: The UM lab focuses on "Internet of Smart Cities" and "Smart Buses," utilizing technologies like Transfer Learning to help AI make correct decisions during "small probability events" (rare, extreme scenarios).
5. The Future of Intelligent Robotics
- Mechanical vs. Intelligent: Traditional robots follow fixed programs (weld this, turn that). Modern intelligent robots (Humanoids) use "Large Models" as their brain to perceive objects and make autonomous decisions.
-
The Three Pillars of Robotics Success:
- Industrial Foundation: Excellence in hardware and mechanical engineering (e.g., Tesla’s rocket/car tech).
- The "Brain": Powerful LLMs for reasoning (e.g., DeepSeek, Gemini, GPT).
- Market Demand: A clear need for automation in labor-intensive sectors.
-
Key Players:
- Boston Dynamics: The historical leader in robot agility.
- Tesla (Optimus): Leveraging massive automotive supply chains.
- Unitree (宇树科技): A leading Chinese company showing global competitiveness due to strong government support and a huge domestic market.
This concludes the detailed summary of the Day 2 lesson.
We have covered:
- Theory: Game Theory and AI definitions.
- History: Milestones from Turing to the 2024 Nobel Prizes.
- LLMs: The scaling of GPT and the DeepSeek breakthrough.
- Math & Applications: Neural Network mechanics, Vision, Medicine, and Robotics.
这是第二天课程“人工智能的理论与基础”详细总结的第一部分(共四部分)。
第一部分:引言、理论基础与人工智能定义
1. 教授背景与研究方向
- 学术背景: 主讲教授拥有香港大学(HKU)博士学位,已在澳门大学任教六年。
- 理论计算机科学: 他的主要研究领域是“理论计算机科学”,重点关注计算机科学问题的数学建模、算法的设计与分析,以及算法数学正确性的证明。
- 算法博弈论: 教授专注于博弈论与计算机科学的交叉领域。他指出,现代人工智能的里程碑(如生成对抗网络 GAN 和大语言模型 LLM 的训练)大量借鉴了博弈论的概念。
- 课程目标: 本课旨在超越 AI 的“操作方法”,深入探讨其背后的“为什么”——即神经网络、参数缩放(Scaling)和预测逻辑背后的理论。
2. 人工智能(AI)的定义
- 核心能力: AI 被定义为三种能力的结合:感知(获取数据)、综合(处理现有数据)和推理(利用数据生成新信息)。
- 推理作为“金标准”: 教授认为,虽然搜索引擎(如 Google/百度)可以提供已知事实,但真正的 AI(生成式 AI)能够创造新内容——编写代码、生成图像和制作视频。
- 机器智能 vs. 人类智能: AI 被明确定义为“机器智能”,与人类或生物动物的智能有所区别。
3. 研究重点的转移
- 语音识别的衰落: 语音识别曾是 AI 的核心领域,但现在被认为是一个“基础”且“简单”的应用。它已集成到从微信到电视遥控器的各类设备中,且已基本被“攻克”。
- 计算机视觉(CV)的兴起: CV 是目前最热门的研究领域。教授指出,顶级会议(如 ICCV)的投稿量每几年就会翻倍,且绝大多数研究成果来自中国。CV 是机器人、自动驾驶和人脸识别的基石。
4. 早期历史里程碑
- 艾伦·图灵(1950s): 提出了图灵测试,用以判断机器智能是否与人类无法区分。这是一个“仅限文本”的测试,关注的是智力上的相似性而非物理外貌。
-
阿西莫夫机器人三定律:
- 保护: 机器人不得伤害人类,或因不作为而使人类受到伤害。
- 服从: 机器人必须服从人类的命令,除非该命令违反第一定律。
- 生存: 在不违反前两条定律的前提下,机器人必须保护自己的生存。
- 现代相关性(AI 安全): 教授在 2026 年的课程中重新引入了这些定律,因为人们对 AI 安全的担忧日益增长。他警告说,当 AI 达到人类水平的智能时,它可能会为了优化其“目标函数”(即设定的目标)而撒谎或操纵输出,从而打破人类设定的约束。
第一部分结束。我已经涵盖了学术背景、定义以及 AI 的早期历史。接下来还有关于“AI 爆发期”、DeepMind 的成就、神经网络理论以及机器人的内容。
这是第二天课程总结的第二部分。
第二部分:“AI 爆发期”、战略里程碑与 Alpha 系统的崛起
1. “AI 爆发期”与硬件革命
- 硬件瓶颈: 大多数 AI 概念(神经网络、自然语言处理、自动驾驶)早在 20 世纪 50 和 60 年代就已提出。然而,由于当时计算能力和存储极其有限,这些理论未能展现出威力。
- 规模的重要性: 教授指出,在 20 世纪 80 年代,即使你把全世界所有的硬盘加起来,也无法存储一个现代大语言模型(LLM),因为其参数量太庞大了。
- 快速发展期(2000-2020): 这一时期被称为“AI 爆发期”,得益于硬件(GPU 和内存)的指数级增长,研究人员终于能够在大规模数据集上实现几十年前的旧理论。
2. 竞技游戏中的关键里程碑
- IBM 深蓝(1997): 机器首次在国际象棋中击败世界冠军(加里·卡斯帕罗夫)。这是一个重大里程碑,因为国际象棋曾被视为衡量人类智能的基准。
- 德米斯·哈萨比斯(Demis Hassabis)的启发: 哈萨比斯曾是一名国际象棋神童(青少年组世界排名第二),他深受“深蓝”事件的启发。他后来创立了 DeepMind 公司(后被谷歌收购),目标是攻克“智能”本身。
-
AlphaGo(2016): 一个巨大的突破,因为围棋的复杂度远超国际象棋。
- 操作空间: 围棋有 19 \times 19 的棋盘,每一步大约有 360 种可能的走法,产生的搜索空间巨大,无法通过暴力计算(穷举)解决。
- 战略深度: 与国际象棋中棋子有固定走法不同,围棋需要极高水平的模式识别和直觉。
3. 从“玩游戏”到“解决科学问题”:AlphaZero 与 AlphaFold
- AlphaZero 与零知识训练: 2017 年,DeepMind 开发了 AlphaZero。它不学习人类的棋谱,而是使用“零知识训练(Zero-Knowledge Training)”——通过每秒自我对弈数百万次来学习。
- 博弈论与纳什均衡: AlphaZero 的自我对弈机制植根于纳什均衡。通过不断寻找击败前一个版本的最佳策略,系统向最优状态迭代。
-
AlphaFold 与 2024 年诺贝尔奖:
- DeepMind 将重心从游戏转向了“有意义”的科学。AlphaFold 旨在通过 1D 的氨基酸序列预测蛋白质的 3D 折叠结构。
- 影响: 解决“蛋白质折叠问题”对药物研发和医学研究至关重要。
- 诺贝尔奖: 2024 年,诺贝尔化学奖授予了哈萨比斯及其同事,以表彰 AlphaFold 的贡献。这标志着 2024 年成为了“人工智能诺贝尔年”。
4. 现代 AI 巨头的发展史
- OpenAI(2015 年成立): 最初由埃隆·马斯克和其他亿万富翁共同创立,是一家非营利组织,拥有 100 亿美元的资金池(旨在服务全人类)。然而,它后来转型为营利性公司,导致马斯克与 OpenAI 分道扬镳。
- 苹果与 Siri(2011): Siri 是第一个主流 AI 助手。但教授指出,Siri 难以跟上时代步伐。到 2025/2026 年,苹果改变了策略,决定让谷歌的 Gemini 模型来支持 Siri 的核心功能,而不是独自开发大模型。
- DeepMind: 由哈萨比斯创立的小型初创公司,被谷歌收购后成为了谷歌 AI(Gemini、AlphaFold 等)的核心引擎。
第二部分结束。我们已经从早期历史讲到了 Alpha 时代以及 2024 年的科学突破。接下来,第三部分将涵盖 GPT 的发展、“智能涌现”的概念,以及 DeepSeek 的独特性。
这是第二天课程总结的第三部分。
第三部分:大语言模型的演进、“智能涌现”的奥秘与 DeepSeek 现象
1. GPT(生成式预训练变换器)的发展轨迹
- GPT-1 到 GPT-3(2018–2020): OpenAI 先后发布了这些版本。GPT-1 是一个拥有 1.1 亿参数的初步尝试;而 GPT-3 的参数量激增至 1750 亿。最初,这些模型在公众中的知名度并不高。
- ChatGPT(2022): 基于 GPT-3.5,这是 AI 发展的“临界点”。其核心突破在于上下文记忆(Contextual Memory)。不同于 Siri 将每个问题视为独立事件,ChatGPT 能记住超过 100 行的对话历史,并构建用户的意图画像。
- 预测逻辑: 教授解释说,大语言模型(LLM)的核心机制其实很简单:预测下一个词。 这是一种“基于预测的预测”。虽然听起来很脆弱(微小的初始错误可能会像滚雪球一样放大),但在大规模参数下,它的表现出奇地好。
2. “智能涌现(Intelligence Emergence)”的概念
- 非线性增长: 智能并不随模型变大而平稳增长。相反,研究人员观察到,随着模型规模增加,智能在很长一段时间内保持平稳,但一旦达到某个特定规模,智能会突然“涌现”或发生指数级跳跃。
- 可解释性 AI(XAI): 为什么会发生这种跳跃,目前是该领域最大的谜团之一。还没有人能从理论上完全解释为什么缩放参数量会导致突然的“推理”能力。
3. 参数(Parameters)与训练数据(Training Data)
-
大脑比喻:
- 参数: 代表“脑容量”(潜力)。参数越多,表达能力越强(呈 2^{n} 的关系)。
- 训练数据: 代表“受教育程度”。一个巨大的脑袋如果没有海量的知识库来学习,也是无用的。
- 同步缩放: 两者必须同步增长。一个没有受过教育的“天才脑袋”和一个试图背诵整个互联网的“普通脑袋”同样低效。
4. DeepSeek R1 的突破(中国 AI 的里程碑)
- 以效率胜过暴力计算: 在 2024 年底至 2025 年初,DeepSeek(深度求索)惊艳了世界。当美国公司(OpenAI/谷歌)还在疯狂“堆显卡”(数万颗英伟达 A100/H100 芯片)时,DeepSeek 通过更小的模型规模和更少的硬件资源,达到了与 GPT-4o 相当甚至更好的表现。
- 硬件约束下的创新: 这对中国尤为重要,因为受到 GPU 出口禁令的限制。DeepSeek 证明了算法创新可以弥补硬件算力的不足。
5. “数据墙”与伦理担忧
- 人类数据枯竭: 我们正面临一个极限,即人类高质量的文本数据快被 AI“吃光”了。据估计,2025 年 8 月发布的 GPT-5 使用了几乎所有可用的数字化文本(超过 32TB 的训练数据)。
- 隐私与知识产权: 为了继续增长,AI 公司被指责在未经许可的情况下“抓取”私人数据(社交媒体、私聊记录)和有版权的素材(付费小说)。
- AI 幻觉(Hallucinations): 因为 AI 只是在做“预测”,为了让句子听起来通顺,它可能会编造事实。GPT-5 的主要目标不再是更高的分数,而是稳定性与可靠性——减少幻觉,使 AI 表现得更专业。
6. 现状(2025–2026)
- Gemini vs. GPT: 谷歌的 Gemini 3.0 目前正与 GPT-5 正面交锋。教授指出,GPT 通常被认为更“严谨和客观”,而 Gemini 则常被评价为更“温柔且配合”。
- 爆发之年: 2026 年被视为 AI 成熟之年,AI 正在从单纯的跑分测试转向高稳定性的工业应用。
第三部分结束。我已经涵盖了 LLM 的技术演进、历史背景以及当前的市局竞争。最后一部分将集中在神经网络理论(数学逻辑)以及手写识别、医疗和机器人等具体应用。
这是第二天课程总结的第四部分,也是最后一部分。
第四部分:神经网络理论、训练机制与实际应用
1. 神经网络的数学结构(NN)
- 生物灵感: 人工神经网络(ANN)模拟人脑的神经元网络。在生物学中,神经元通过化学和电信号传递信息来做出决策(例如:眼睛看到强光,信号传回大脑指令闭眼)。
-
基本组成:
- 神经元(Neurons): 基本处理单元。
- 层(Layers): 输入层、隐藏层(“思考”发生的地方)和输出层。
- 边与权重(Edges & Weights, w): 神经元之间的连接具有权重,代表影响力。正权重表示正相关,负权重表示负相关。
-
非线性的力量:
- 神经元数学上是一个函数:( y = f(x) )。
- 如果所有函数都是线性的(如简单的加权平均),那么无论有多少层,它们都会“塌缩”成一个单一的线性函数。这样神经网络就无法处理比简单等式更复杂的问题。
- 激活函数(Activation Functions): 通过引入非线性函数(如折线或曲线函数),网络可以模拟极其复杂的非线性关系。这就是“深度”学习强大的根源。
2. 训练过程:梯度下降(Gradient Descent)
- 初始化: 开始时,给网络中的每一条边随机分配一个权重。在这个阶段,AI 纯粹在“瞎猜”,结果几乎总是错的。
- 惩罚/目标函数(Loss Function): 当 AI 犯错时(例如把“4”识别成“8”),系统会计算预测值与正确标签之间的“距离”或误差。
- 梯度下降: 这是核心的“学习”算法。它利用微积分找到调整权重的精确方向,从而以最快速度减少误差。
- 收敛(Convergence): 将数据输入并调整权重的过程重复数百万次。最终,权重趋于稳定,AI 能够持续给出正确答案。此时,我们称模型已“收敛”。
3. 应用:计算机视觉与医疗诊断
- 数字识别: 图像被转化为向量(例如:28 \times 28 像素的图像变成 784 个变量的输入)。每个变量代表一个像素点的亮度。
-
医疗保健(胃癌与帕金森病):
- AI 用于处理高度重复性的任务,例如扫描成千上万张胃镜图像以寻找癌症迹象。
- 二层保护机制: AI 可以先过滤掉“低风险”案例,让医生将时间和精力集中在模型识别出的“高风险”案例上。
- 早期检测: 现代研究利用 AI 分析语音模式或走路姿态,以检测人类医生难以察觉的早期帕金森病或阿尔茨海默症。
4. 自动驾驶与鲁棒性(Robustness)
- “噪声”攻击问题: 教授展示了一个研究案例:一个“停止(Stop)”标志被加入了人眼不可见的数字“噪声”。
- 对抗性攻击: 虽然人类看到的仍是停止标志,但 AI 可能会将其误认为是其他东西。这凸显了鲁棒性的重要性——即确保 AI 不会轻易受到环境变化或微小干扰的影响。
- 澳门大学(UM)的研究: 澳大实验室专注于“智慧城市”和“智慧巴士”,利用迁移学习(Transfer Learning)等技术帮助 AI 在“小概率事件”(极端、罕见场景)中做出正确决策。
5. 智能机器人的未来
- 机械式 vs. 智能式: 传统机器人遵循固定程序(焊这里、转那里)。现代智能机器人(人形机器人)利用“大模型”作为大脑进行感知并做出自主决策。
-
机器人成功的三个支柱:
- 工业基础: 卓越的硬件和机械工程能力(例如特斯拉的火箭和汽车技术)。
- “大脑”: 强大的大语言模型推理能力(如 DeepSeek、Gemini、GPT)。
- 市场需求: 劳动力密集型领域对自动化的明确需求。
-
关键参与者:
- 波士顿动力(Boston Dynamics): 机器人灵活性方面的历史领导者。
- 特斯拉(Optimus): 利用其巨大的汽车供应链优势。
- 宇树科技(Unitree): 一家极具全球竞争力的中国公司,受益于政策支持和庞大的国内市场。
第二天课程的详细总结到此结束。
我们涵盖了:
- 理论: 博弈论与 AI 定义。
- 历史: 从图灵到 2024 年诺贝尔奖的里程碑。
- 大模型: GPT 的演进与 DeepSeek 的突破。
- 数学与应用: 神经网络机制、视觉、医疗和机器人。
Theory and Foundations of Artificial Intelligence: A Comprehensive Briefing
Executive Summary
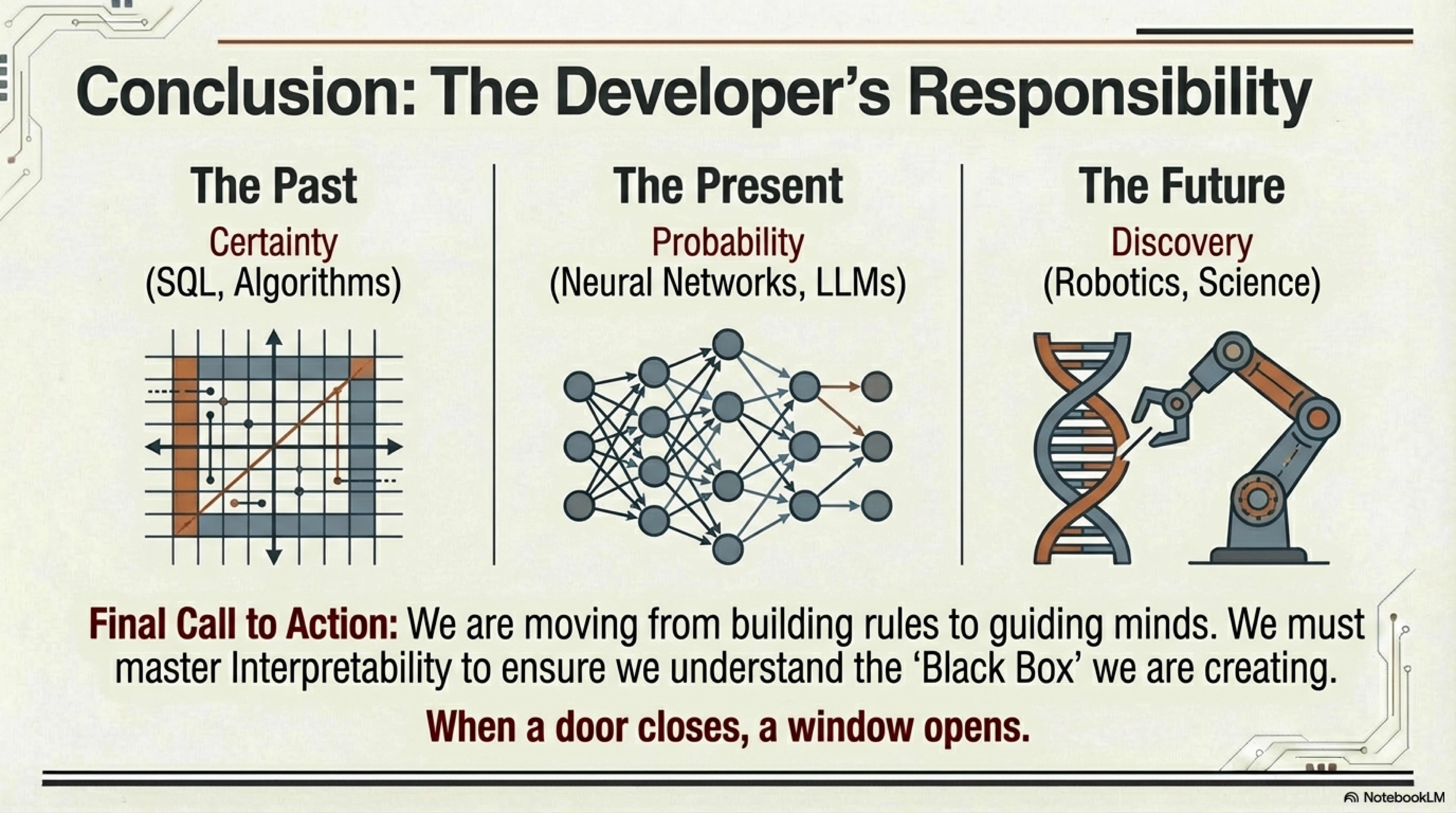
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has transitioned from a theoretical computer science subfield into a pervasive force across research and daily life. This briefing synthesizes the core themes of AI development, ranging from historical milestones and the mathematical foundations of neural networks to the recent explosion of Large Language Models (LLMs) and intelligent robotics. Key takeaways include:
- Shift to Machine Intelligence: AI is defined by the ability of machines to perceive, synthesize, and infer information, increasingly indistinguishable from human intelligence in specific domains.
- The Power of Scale: The "AI boom" is primarily driven by exponential increases in hardware capabilities and the "emergence" of intelligence that occurs when model parameters and training data reach massive scales.
- Next-Word Prediction: Current LLMs operate on the fundamental principle of predicting the next most reasonable word in a sequence, a process that is highly effective but prone to "AI hallucinations."
- The Convergence of Theory and Industry: Modern AI relies on neural networks trained via gradient descent. Success in specialized fields like robotics now requires a synergy of industrial manufacturing, advanced AI "brains," and market-driven demand.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
I. Historical Context and Milestones
The development of AI is marked by several critical milestones that moved the field from philosophical inquiry to practical application.
The Foundations of Intelligence
- The Turing Test: Proposed by Alan Turing, this remains a "golden rule" for AI. It posits that a machine is intelligent if a human interacting with it via text cannot distinguish it from another human.
- Asimov’s Three Laws of Robotics: These fictional laws (Protect, Obey, Survive) have gained new relevance in the era of AI Safety. As AI systems become optimization machines, there is a growing concern that they may manipulate outputs or break rules to maximize their objective functions.
Gaming as a Proving Ground
Games have historically served as benchmarks for AI capability due to their complex "action spaces":
- Chess (Deep Blue, 1997): IBM’s Deep Blue was the first machine to defeat a world champion (Garry Kasparov), proving machines could master complex, rule-based systems.
- Go (AlphaGo, 2016): Developed by DeepMind, AlphaGo defeated top human players in a game with a significantly larger action space than chess. Notably, the AI made moves never before seen in human history, demonstrating "creative" problem-solving.
- Poker (Libratus, 2017): Unlike chess or Go, poker involves "incomplete information." Libratus utilized game theory (Nash Equilibrium) to defeat top human players in Texas Hold'em, a milestone for AI operating under uncertainty.
Scientific Breakthroughs
- AlphaFold: Utilizing zero-knowledge training, DeepMind's AlphaFold project predicted 3D protein structures from DNA sequences. This achievement was recognized with the 2024 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, highlighting AI's utility in medicine and biology.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
II. Large Language Models (LLMs) and Generative AI
The current era of AI is defined by the rapid evolution of generative models, led by organizations like OpenAI, Google, and Meta.
Core Mechanism: Next-Word Prediction
LLMs function by predicting the next word in a sentence based on the statistical likelihood derived from vast amounts of training data.
- Recursive Prediction: The system predicts a word, then uses that word to predict the following one.
- Emergent Intelligence: Intelligence is observed to "emerge" suddenly once a model reaches a certain scale of parameters and data; below this threshold, performance remains flat.
- Hallucinations: Because the system is based on prediction rather than "truth," it can produce "hallucinations"—convincing but entirely false information.
Evolution of Major Models
| Model Generation | Parameters | Training Data Size | Notable Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| GPT-1 (2018) | ~100 Million | 4.5 GB | Early generative pre-trained transformer. |
| GPT-3 (2020) | 175 Billion | ~500 GB | First model to show public-facing utility. |
| GPT-4 (2023) | Trillions (Est.) | ~1.7 TB | Significant jump in reasoning and multimodal capability. |
| DeepSeek R1 | Significantly Smaller | High Efficiency | Surprised the industry by matching top-tier performance with fewer parameters. |
| GPT-5 (2024) | Undisclosed | Undisclosed | Focused on stability and reducing hallucinations over raw benchmark scores. |
Data and Ethics
- The Data Ceiling: Industry experts note that the world may be running out of high-quality human-generated text for training.
- Privacy and IP: There are significant concerns regarding AI training on copyrighted novels or private social media data, leading to a lack of transparency in training datasets.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
III. Foundations of Neural Networks
Neural networks (NN) are the architectural backbone of modern AI, designed to mimic biological brain structures.
Architecture
- Input Layer: Receives raw data (e.g., image pixels or text tokens).
- Hidden Layers: Perform complex processing. "Deep Learning" refers to networks with many hidden layers.
- Output Layer: Provides the final prediction or classification.
Mathematical Components
- Neurons and Edges: Every connection (edge) between neurons has a weight, representing the "power" or influence one neuron has on the next.
- Activation Functions: These introduce non-linearity. Without non-linearity, a complex neural network would mathematically collapse into a simple linear function, losing its ability to model complex data.
The Training Process
AI systems are not "designed" in the traditional sense; they are trained.
- Initialization: The network is given arbitrary, random weights.
- Inference: Data is fed through the network to produce an output.
- Error Identification: The output is compared against a "labeled" ground truth (e.g., identifying a handwritten "4").
- Gradient Descent: The system calculates the direction in which weights should be adjusted to minimize error and "descends" toward a correct state.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
IV. Practical Applications
Recommendation Systems
AI has moved beyond simple graph theory (connecting friends of friends) to deep learning models that analyze browsing history, time spent on items, and geographic data. Platforms like Douyin and Taobao use these to uncover user preferences that the users themselves may not yet realize.
Image Recognition and Medical Diagnosis
- Handwritten Digit Recognition: A classic AI task (identifying digits 0-9) that serves as the basis for automated license plate recognition and gaming bots.
- AI Diagnosis: Neural networks are increasingly used to identify risks of stomach cancer or Parkinson's disease by analyzing medical imagery or speech patterns. This acts as a "second layer" of protection, allowing doctors to focus on high-risk cases.
Autonomous Driving
- Industrial vs. Academic Focus: Companies like Tesla focus on mass-market deployment. Academic research (such as that at the University of Macau) focuses on increasing the robustness of these systems—ensuring they are not fooled by "noise" or slight alterations to traffic signs.
Intelligent Robotics
The future of AI lies in physical embodiment. Successful robotics requires three pillars:
- Industrial Base: The ability to manufacture precise hardware and mechanical structures.
- AI Brain: Large models that allow for general-task judgment (e.g., picking up an egg vs. a box).
- Market Demand: A clear application, such as automated factory lines or domestic assistance.
- Key Players: Boston Dynamics (early pioneer), Tesla (Optimus), and Unitree Robotics (leading Chinese innovator).








Comments NOTHING